

Most cells in your body (and those of all other living things) spend most of their lives in interphase. Liver cells are detoxifying the blood, nerve cells are sending and receiving electrical impulses, skin cells are forming a barrier to the outside world and protecting your inside bits and pieces. During interphase, cells are going through their normal daily cell routines. The cell cycleĪll cells go through the life stages that we call the cell cycle. In lab, you’ll model these processes with models and practice using the necessary terms to keep track of chromosomes! To prepare, you’ll read the general information on how these processes work so you can come to lab ready to apply your knowledge and see mitosis under the microscope. If you are having trouble with these processes, this lab should help. How many chromosomes are involved in each process? Where did the chromosomes come from what happens to them how does it happen and why is it necessary for all these things to take place? And, perhaps most importantly, how can I remember all this stuff? This lab is designed to make sense out of eukaryotic cell division. Many questions often arise when learning these processes. Takes part in the formation of gametes and maintenance of chromosome number.The processes by which cells divide are complicated and there are a lot of details to remember. Genetic diversity through sexual reproduction. Two chromatids of a chromosome do not exchange segments during prophase.Ĭhromatids of two homologous chromosome exchange segments during crossing over.Ĭellular reproduction and general growth and repair of the body. Synapsis of Homologous chromosomes takes place during prophase. Prophase is comparatively longer and may take days.
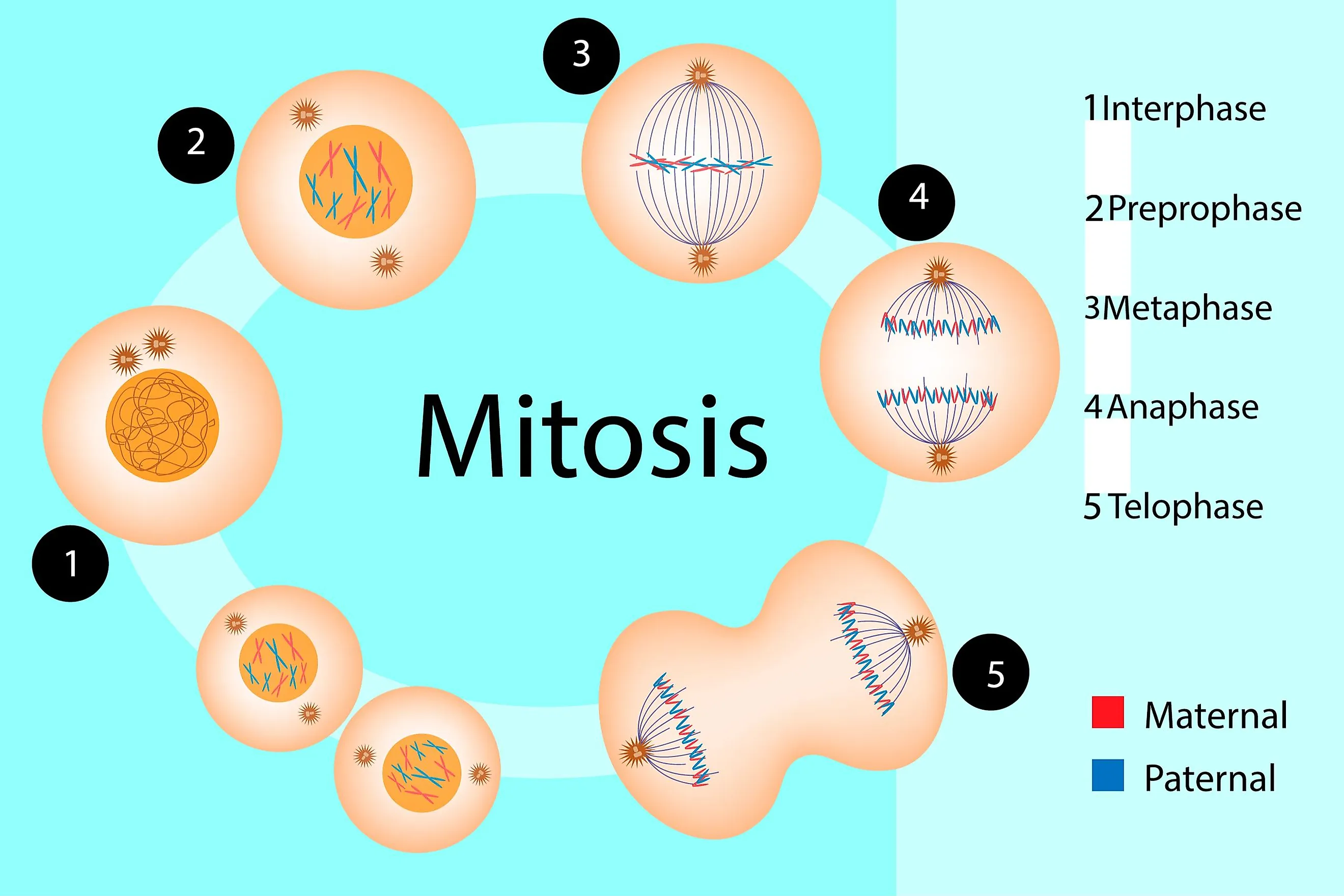
The centromeres do not separate during anaphase I, but during anaphase II.ĭuration of prophase is short, usually of few hours. Occurs in Telophase I and in Telophase II. (Meiosis 1) Prophase I, Metaphase I, Anaphase I, Telophase I (Meiosis 2) Prophase II, Metaphase II, Anaphase II and Telophase II. Prophase, Metaphase, Anaphase, Telophase. Observed during prophase I and metaphase I.ĭo not disappear completely in telophase I. Sex cells only: female egg cells or male sperm cells.
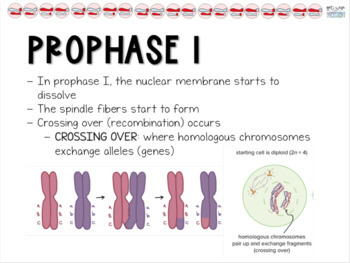
Takes place during zygotene of prophase I and continue upto metaphase I. Following are the differences between Mitosis and Meiosis: S.N. Meiosis is a type of cellular reproduction in which the number of chromosomes are reduced by half through the separation of homologous chromosomes, producing two haploid cells. Mitosis is a process of asexual reproduction in which the cell divides in two producing a replica, with an equal number of chromosomes in each resulting diploid cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
